By Steve Sailer
09/07/2015
Commenter Romanian calls our attention to this relevant passage from Edward Gibbon’s The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire about the decision of the Emperor Valens in 376 A.D. to permit — and even assist — the crossing of the Danube, until then the frontier of Roman civilization, by German barbarians.
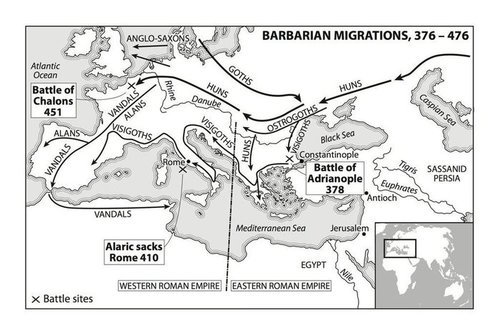
In the opinion of Gibbon, the subsequent defeat and death of the Emperor Valens at the hands of the Germans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378 marked the beginning of the Fall of the Roman Empire in the West.
Gibbon narrates:
In the disastrous period of the fall of the Roman empire, which may justly be dated from the reign of Valens, the happiness and security of each individual were personally attacked; and the arts and labors of ages were rudely defaced by the Barbarians of Scythia [Huns] and Germany [Goths]. The invasion of the Huns precipitated on the provinces of the West the Gothic nation, which advanced, in less than forty years, from the Danube to the Atlantic, and opened a way, by the success of their arms, to the inroads of so many hostile tribes, more savage than themselves. …Indeed.But the attention of the emperor [Valens] was most seriously engaged, by the important intelligence which he received from the civil and military officers who were intrusted with the defence of the Danube. He was informed, that the North was agitated by a furious tempest; that the irruption of the Huns, an unknown and monstrous race of savages, had subverted the power of the Goths; and that the suppliant multitudes of that warlike nation, whose pride was now humbled in the dust, covered a space of many miles along the banks of the river.
With outstretched arms, and pathetic lamentations, they loudly deplored their past misfortunes and their present danger; acknowledged that their only hope of safety was in the clemency of the Roman government; and most solemnly protested, that if the gracious liberality of the emperor would permit them to cultivate the waste lands of Thrace, they should ever hold themselves bound, by the strongest obligations of duty and gratitude, to obey the laws, and to guard the limits, of the republic. …
As long as the same passions and interests subsist among mankind, the questions of war and peace, of justice and policy, which were debated in the councils of antiquity, will frequently present themselves as the subject of modern deliberation.
But the most experienced statesman of Europe has never been summoned to consider the propriety, or the danger, of admitting, or rejecting, an innumerable multitude of Barbarians, who are driven by despair and hunger to solicit a settlement on the territories of a civilized nation.Gibbon published Volume II in 1781. A lot has happened since then.
When that important proposition, so essentially connected with the public safety, was referred to the ministers of Valens, they were perplexed and divided; but they soon acquiesced in the flattering sentiment which seemed the most favorable to the pride, the indolence, and the avarice of their sovereign.As The New York Times explained this week, mass migration across the Danube offers the receiving country “an opportunity to rejuvenate its aging demographics and ensure its economic prosperity …”The slaves, who were decorated with the titles of praefects and generals, dissembled or disregarded the terrors of this national emigration; so extremely different from the partial and accidental colonies, which had been received on the extreme limits of the empire.
But they applauded the liberality of fortune, which had conducted, from the most distant countries of the globe, a numerous and invincible army of strangers, to defend the throne of Valens; who might now add to the royal treasures the immense sums of gold supplied by the provincials to compensate their annual proportion of recruits.
The prayers of the Goths were granted, and their service was accepted by the Imperial court: and orders were immediately despatched to the civil and military governors of the Thracian diocese, to make the necessary preparations for the passage and subsistence of a great people …Two years later in 378, the migrants killed Emperor Valens at the cataclysmic Battle of Adrianople.The Imperial mandate was at length received for transporting over the Danube the whole body of the Gothic nation … A probable testimony has fixed the number of the Gothic warriors at two hundred thousand men: and if we can venture to add the just proportion of women, of children, and of slaves, the whole mass of people which composed this formidable emigration, must have amounted to near a million of persons, of both sexes, and of all ages.
… their gay and splendid apparel, their robust and martial figure, excited the surprise and envy of the Provincials. …
An undisciplined and unsettled nation of Barbarians required the firmest temper, and the most dexterous management. The daily subsistence of near a million of extraordinary subjects could be supplied only by constant and skilful diligence, and might continually be interrupted by mistake or accident. The insolence, or the indignation, of the Goths, if they conceived themselves to be the objects either of fear or of contempt, might urge them to the most desperate extremities
… a spirit of discontent insensibly arose in the camp of the Barbarians, who pleaded, without success, the merit of their patient and dutiful behavior; and loudly complained of the inhospitable treatment which they had received from their new allies. They beheld around them the wealth and plenty of a fertile province, in the midst of which they suffered the intolerable hardships of artificial famine. But the means of relief, and even of revenge, were in their hands; since the rapaciousness of their tyrants had left to an injured people the possession and the use of arms. …
“That successful day put an end to the distress of the Barbarians, and the security of the Romans: from that day, the Goths, renouncing the precarious condition of strangers and exiles, assumed the character of citizens and masters, claimed an absolute dominion over the possessors of land, and held, in their own right, the northern provinces of the empire, which are bounded by the Danube.”
Such are the words of the Gothic historian, who celebrates, with rude eloquence, the glory of his countrymen.But the dominion of the Barbarians was exercised only for the purposes of rapine and destruction. …
The imprudence of Valens and his ministers had introduced into the heart of the empire a nation of enemies; …
One of the most dangerous inconveniences of the introduction of the Barbarians into the army and the palace, was sensibly felt in their correspondence with their hostile countrymen; to whom they imprudently, or maliciously, revealed the weakness of the Roman empire. A soldier, of the lifeguards of Gratian, was of the nation of the Alemanni, and of the tribe of the Lentienses, who dwelt beyond the Lake of Constance. Some domestic business obliged him to request a leave of absence. In a short visit to his family and friends, he was exposed to their curious inquiries: and the vanity of the loquacious soldier tempted him to display his intimate acquaintance with the secrets of the state, and the designs of his master. The intelligence, that Gratian was preparing to lead the military force of Gaul, and of the West, to the assistance of his uncle Valens, pointed out to the restless spirit of the Alemanni the moment, and the mode, of a successful invasion. … The boldest hopes of rapine, perhaps of conquest, outweighed the considerations of timid prudence, or national faith. Every forest, and every village, poured forth a band of hardy adventurers …
A great number of brave and distinguished [Rome] officers perished in the battle of Hadrianople, which equalled in the actual loss, and far surpassed in the fatal consequences, the misfortune which Rome had formerly sustained in the fields of Cannae.That was Hannibal’s greatest victory over the Romans, 594 years before Adrianople.
… Whatever may have been the just measure of the calamities of Europe, there was reason to fear that the same calamities would soon extend to the peaceful countries of Asia. The sons of the Goths had been judiciously distributed through the cities of the East; and the arts of education were employed to polish, and subdue, the native fierceness of their temper. In the space of about twelve years, their numbers had continually increased; and the children, who, in the first emigration, were sent over the Hellespont, had attained, with rapid growth, the strength and spirit of perfect manhood. It was impossible to conceal from their knowledge the events of the Gothic war; and, as those daring youths had not studied the language of dissimulation, they betrayed their wish, their desire, perhaps their intention, to emulate the glorious example of their fathers. …Valen’s successor Theodosius the Great (ruled 379-395) stabilized the situation by practicing divide and conquer tactics with the fractious barbarians, recruiting some to uphold his power:A formidable tempest of the Barbarians of Germany seemed ready to burst over the provinces of Gaul; …
But the effects which were produced by the battle of Hadrianople on the minds of the Barbarians and of the Romans, extended the victory of the former, and the defeat of the latter, far beyond the limits of a single day. A Gothic chief was heard to declare, with insolent moderation, that, for his own part, he was fatigued with slaughter: but that he was astonished how a people, who fled before him like a flock of sheep, could still presume to dispute the possession of their treasures and provinces. …
An army of forty thousand Goths was maintained for the perpetual service of the empire of the East; and those haughty troops, who assumed the title of Foederati, or allies, were distinguished by their gold collars, liberal pay, and licentious privileges. Their native courage was improved by the use of arms and the knowledge of discipline; and, while the republic was guarded, or threatened, by the doubtful sword of the Barbarians, the last sparks of the military flame were finally extinguished in the minds of the Romans.They’re demographically vibrant!Theodosius had the address to persuade his allies, that the conditions of peace, which had been extorted from him by prudence and necessity, were the voluntary expressions of his sincere friendship for the Gothic nation. …
The advocates of Theodosius could affirm, with some appearance of truth and reason, that it was impossible to extirpate so many warlike tribes, who were rendered desperate by the loss of their native country; and that the exhausted provinces would be revived by a fresh supply of soldiers and husbandmen.
The Barbarians still wore an angry and hostile aspect; but the experience of past times might encourage the hope, that they would acquire the habits of industry and obedience; that their manners would be polished by time, education, and the influence of Christianity; and that their posterity would insensibly blend with the great body of the Roman people.A decade and a half after Theodosius’s death, the Visigoths sacked Rome in 410, the first time Rome had been sacked in 797 years. And then the Huns arrived, and then the last Roman emperor was deposed in 476, and there was a Dark Age or two.
Notwithstanding these specious arguments, and these sanguine expectations, it was apparent to every discerning eye, that the Goths would long remain the enemies, and might soon become the conquerors of the Roman empire. Their rude and insolent behavior expressed their contempt of the citizens and provincials, whom they insulted with impunity.But everything has worked out fine in the long run, so letting the Barbarians cross the Danube in 376 A.D. was a good idea and a good precedent.
Publishing his first volume in 1776, a mere 1400 years later, Gibbon could look back on the decline and fall of the Roman Empire with witty equanimity. Why can’t we look back on 2015 with the same ironic detachment?
This is a content archive of VDARE.com, which Letitia James forced off of the Internet using lawfare.